HISTORY (VIII)-LESSON-2
FROM TRADE TO TERRITORY
(LESSON NOTES)
_________________________________________________________
v INTRODUCTION
Ø Aurangzeb was the last powerful
Mughal ruler. After the death of Aurangzeb in 1707 , the later rulers proved to
be inefficient and many subadars (governors) established the regional kingdom.
After 17th century many foreign trading companies came to India. They
started to establish the power in India. It makes the revelry among them finally
East India Company won and established their rule here. These lessons focus on
this that how East India Company established its rule in India.
v
EUROPEAN TRADING COMPANIES
NAME OF COMAPNY
|
YEAR
|
COUNTRY
|
FIRST FACTORY
|
OTHER
|
PORTUGUESE
|
1498
|
PORTUGAL
|
CALICAT
|
FIRST PERSON-VASCO DA GAMA
|
EAST INDIA COMAPNY
|
1600
|
ENGLAND
|
SURAT
|
QUEEN- ELIZABETH 1
|
DUTCH EAST INDIA COMPANY
|
1602
|
HOLLAND
|
MASULIPATTANAM
|
|
DENISH EAST INDIA COMPANY
|
1616
|
DENMARK
|
||
FRENCH EAST INDIA COMPANY
|
1664
|
FRANCE
| SURAT |
v WHY THESE COMPANIES CAME-
Ø Cotton and silk produced in India
had a big market in Europe.
 |
| ROUTE TO INDIA |
Ø So these companies purchase these
goods at a cheap price and sold them at higher price in Europe and make profit.
v EAST INDIA
COMAPNY
Ø In 1600 queen Elizabeth I granted
the sole right to trade with the East to East India Company.
Ø When other company comes than English
east India company had to compete with other European companies such as Franch,
Dutch, and Portugese.
Ø Because of the powerful naval force,
British won over other European powers and became the champion of struggle of
monotony of trade.
v EAST INDIA COMPANY BEGINS TRADE IN
BENGAL
Ø In 1651, the first English factory
was set up on the banks of river Hugli and first English factory was opened up
at Surat in 1608.
Ø Aurangzeb issued a Farman granting
the company the right to trade duty-free.
Ø But the company tried to press for
more concessions and manipulate existing privileges. It make the huge loss for
Bengal Nawab.
Ø For trading purpose, the passes were
issued to company officials but they misused these passes for private trade and
accumulate wealth on the name of company.
v
HOW DID TRADE LEAD TO BATTLE OF PLASSEY:
Ø After the death of Aurangzeb, the
Bengal Nawabs asserted their power and autonomy.
Ø Bengal Nawab-Murshid Quli
Khan ,Alivardi Khan and then Sirajuddaulah
Ø The Britishers wanted many
concession as
§ More concession on trade, duties to be
abolished.
§ Wanted fortification of Calcutta
§ Wanted to minted the coins on the
name of Queen
Ø But Bengal nawabs refused to give
the permission which led to war.
v THE BATTLE OF PLASSEY:
Ø When Nawab Sirajjuddaluh refused to
give the rights on 23rd June 1757, Battle of Plassey was fought .
Ø In 1757, Robert Clive led the Company’s
army against Sirajuddaula at Plassey.
Ø Main reason for defeat of the Nawab
was that the forces led by Mir Jafar, one of Sirajuddaulah’s commanders,
betrayed Sirajuddaula and never fought the battle.
Ø Mir Jafar was promised by Clive to
be made Nawab after crushing Sirajuddaulah.
Ø As par the deal Mir Jafar became the
Nawab of Bengal after the defeat and death of Sirajuddaula. But he was the
nominal head of Bengal and actual power remained in the hands of British.
v THE BATTLE OF BUXAR-1764
Ø After the defeat at Plassey,
Sirajuddaulah was assassinated and Mir Jafar was made the Nawab.
Ø Mir Jafar was just a puppet in the
hands of Britishers. When he cnnot complete the demands of Britishers Mir Qasim
was throned.
Ø Mir Qasim abolished the trade duty
for everyone and transfered his capital from Murshidabad to Mungair. But this
was against the interest of British and they declared war.
Ø In 1764, the battle of Buxar was
fought between Britishers and Mir Qasim, when Mir Qasim denied the
privilages given to Britishers.
Ø In this battle Mir Qasim, the Nawab
of Bengal; Shujauddaula, the Nawab of Awadh and Shah Alam the Mughal King
fought against British and British forces were led by Hector Munro.
Ø In this battle British become
victorious and they decided to control the territory by there own.
v
COMPANY OFFICIALS BECOME ‘NABOBS
Ø In 1764, Robert Clive was appointed
Governor of Bengal.
Ø In 1765, the Mughal emperor
appointed the company as the Diwan of the provinces of Bengal and they also got
the Diwani rights of Bihar and Odisha.
Ø ‘Nabobs’-an anglicized version of
the Indian word Nawab as British were leading a levish life similar to nawabs
and everyone was on the mercy of British.
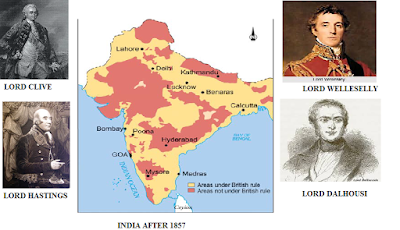
v EXPANSION OF COMPANY RULE:
Ø The process of annexation of Indian
states by the East India Company from 1757 to 1857 brought by different
policies and war.
Ø SUBSIDIARY ALLIANCE’
§ The subsidiary alliance was started
by Lord Wellesley in 1798.
§ According to the alliance, the
company appointed residents in Indian states and the king had to put an army of
British on their own expenditure.
§ In the case of nonpayment to army
the nawab or the king had to give some part of its territory.
§ Many territories were annexed as-Haydrabad,
Tanjore,Awadh, Pune, Indore etc.
Ø ANGLO MYSORE WAR
§ Mysore become powerful under the
ruler Haidar ali(1761-82 and his son Tipu Sultan(1782-1799)-Tiger of Mysore
§ Britisher wanted to trade of spices
but the Mysore rules don’t allow them so there was a quarrel between them.
§ Tipu Sultan also took the help
of French to modernise his army and sent foreign delegates to gether the
foreign help against British.
§ Four wars were fought between
Britishers and Mysore and were known as the Anglo-Mysore wars(1767-1769,
1780-84, 1790-92 and 1799).
 |
| TIPU TOY TIGER |
§ In 1799, the Britishers won the
battle of Seringapatam against Mysore. Tipu Sultan was killed defending his
capital Seringapatam.
§ After that Mysore was placed under Wodeyars and a subsidiary
alliance was imposed on the state.
Ø ANGLO – MARATHA WARS
§ After the defeat of Maratha in
battle of Panipat in 1761, they get divided in various small dynasties such as Peshwa,
Sindhia, Holkars, Gaikwad and Bonsle.
§ Three wars were fought between
Marathas and British in 1782, 1803-05 and 1817-19.
§ The third war was the decisive war
and after this peshwa was deposed and the sent to Bithur near
Kanpur on a pension and imposed subsidiary
alliance on them.
Ø CLAIM TO PARAMOUNTCY
§ As British were proving themselves
as the best power across the India, this enhanced their desire to rule whole
territories and they started direct conquest under lord Hastings
(1813-23).
§ British also wanted to sercure North
West front of their empire in India. For this they fought wars with Afganistan
and Punjab(Anglo Sikh War) and finally won over its territories in 1843
and 1849 respectively.
Ø ABOUT RANI
CHANNAMMA OF KITOOR (in Karnataka today)
§ So
Rani Channamma led an anti-British resistance movement when Britishers
tried to annex the small state of Kitoor .She was arrested in
1824 and died in prison in 1829. But Rayanna,
a poor chowkidar of Sangoli in Kitoor, carried
on the resistance. With popular support he destroyed
many British camps and records. He was caught
and hanged by the British in 1830.
Ø DOCTRINE OF LAPSE
§ This policy was adopted by Lord
Dalhousie (1848-56)
§ According to this policy, the rulers
who do not have any legal heir could not pass on their property to the adopted
son and it would be taken over by British.
§ Many areas were annexed under this
policy as Satara (1848), Nagpur, Sambhalpur (1850), Jhansi (1854).
v ADMINISTRATION UNDER BRITISH
Ø British territories
were broadly divided into administrative units called Presidencies. There were
three Presidencies: Bengal, Madras and Bombay.
Ø Each was ruled
by a Governor. The supreme head
of the administration
was the
Governor-General.
Ø In 1773, Warren Hastings become the
Governor General of Bengal and controlled the governors of other presidencies
of Madras and Bombay.
Ø Separate civil and criminal courts
were set up under the supervision of collector.
Ø New set of laws were compiled by
muftis and Brahmins for the religious interpretation.
Ø The principal
figure in an Indian district was the Collector. His main work was to collect
revenue and taxes and maintain law and order.
v COMPOSITION
OF COMPANY’S ARMY
Ø Initially British India
Company adopted the same method of soldiers
as Mughal have. Their army composed of cavalry (sawars:
trained soldiers on horseback) and infantry.
Ø They were given
training in archery (teer-andazi ) and the use of the sword.
Ø But after 1820 there were some
changes adopted by Britishers as
§ The cavalry
requirements of the Company’s army declined.
§ soldiers were
armed with new weapons as muskets and matchlocks.
§ British began to
develop a uniform military culture.
§ Soldiers were subjected
to European-style training, drill and discipline that regulated their life far
more than before.
v TIME LINE
Ø 1498-Vasca-da gama Reached India
|
Wars
|
Ø 1600- East India company came to
India
|
ANGLO-MYSORE
WAR-
|
Ø 1707- Aurangzeb death
|
I-1767-69
|
Ø 1761-Panipat III battle
|
II-1780-84
|
Ø 1765 Company become Diwan
|
III-1790-92
|
Ø 1773-First governor general
|
IV-1799
|
Ø 1782- The Treaty of Salbai
|
ANGLO
MARATHA WAR
|
Ø 1798 –Subsdiary allianace
|
I-1767-72
|
Ø 1838-Afghan war-1
|
II-1801-03
|
Ø 1842-Afghan war-II
|
III-1817
|
Ø 1848-Doctrine of lapse
|
SIKH
WAR
|
Ø 1856-Awadh Annexed
|
1-1839-42
|
Ø 1857-Revolt
|
II-1848-49
|
Ø 1858-End Of Mughal dynasty
|
PLASSY
WAR-1757
|
Ø
|
BUXAR
WAR-1764
|
Ø
|



Fantastic sir, very helpful
ReplyDeleteVery good Post, thank you.
ReplyDeleteDhakshinavarti Sankha
Lakshmi Shankh
Valampuri Right Handed Shankh